
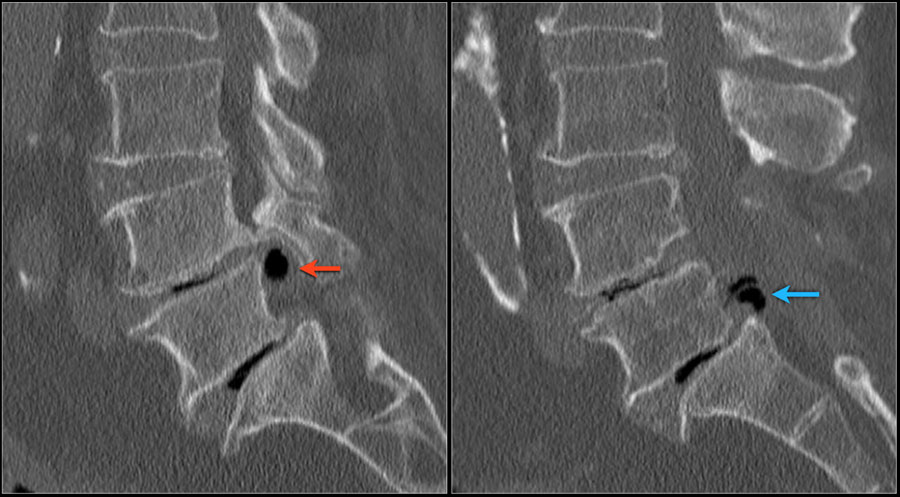
With Type II herniation, the discs become hardened and fibrous over a long period of time and eventually break down, bulge out, and compress the spinal cord. This is most common in small dog breeds with long backs and short legs. Any forceful impact such as jumping and landing, or even just stepping the wrong way, can cause one or more disc(s) to burst and the inner material to press on the spinal cord. This damages the disc, allowing it to break down easier. In Type I, common in the mid-back region of smaller breeds, discs develop a hardening (or calcification) of the outer layer. Type I and Type II of IVDD have different root causes. Loss of bladder and/or bowel control ( urinary and fecal incontinence) or unwillingness to posture to eliminate Pain and weakness in rear legs (lameness) Type II generally has less severe signs and symptoms. There are two types of disc herniation seen in dogs: Type I and Type II. (See Surgery for a Herniated Disc.Made up of a gelatinous substance surrounded by a thick outer layer, intervertebral discs are basically the shock absorbers of the spine. Minimally invasive surgery means a quick recovery, less pain, and less scarring. Surgery for a herniated disc is best performed at a major spine center with doctors trained and experienced in the most up-to-date, minimally invasive techniques. The incision is smaller, and avoids muscle trauma, which allows patients to resume regular activity within a short period of time. Minimal access surgery causes much less trauma than older surgical methods and requires much less time in the hospital. “Minimal access surgery” refers to the advanced techniques that top spine surgeons use to repair a herniated disc. Pain is so severe that it is debilitating.Conservative treatments prove ineffective.Surgery for slipped discs may be recommended if: The spine team at the Weill Cornell Brain and Spine believes in an interdisciplinary approach to the treatment of ruptured discs, including physiatry, pain management, physical therapy, and - only when necessary, minimally invasive surgery. If these initial treatments are ineffective, other options will be considered. In most cases, the symptoms will resolve within 4-6 weeks. Treatment options are usually quite conservative at first, and can include bed rest, time, acupuncture, over-the-counter pain medications, steroids, muscle relaxants, occupational therapy, and injections. Treatments for ruptured discs vary, depending on the location and severity of damage.
#Slipped disk xray full#
Once a diagnosis has been confirmed, an individual with a herniated disc should be referred to a major spine center for a full evaluation and individual treatment plan. It may identify if there is nerve damage or nerve compression. Usually a CT scan follows the Myelogram.Įlectromyogram and Nerve Conduction Studies (EMG/NCS): This test measures the electrical activity in the nerves and muscles. Myelogram: This special x-ray uses dye, which is injected into the spinal fluid. An MRI scan can also show evidence of previous injuries that may have healed and other details in the spine that can’t normally be seen on an x-ray. An MRI uses magnetic fields and radio-frequency waves to create an image of the spine, and can reveal the details of the disc, the nucleus (the jelly-like substance within) and the annulus ( the firm outer layer). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are the best tools for diagnosing a slipped disc. A CT scan may show evidence of a ruptured disc. If a slipped disc is suspected, the physician will usually order imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis.Ĭomputerized tomography (CT) is a noninvasive procedure that uses x-rays to produce a three-dimensional image of the spine. The physician will gather history and symptoms and conduct a physical examination. A normal disc is shown at bottom.Ī herniated disc is often diagnosed by a physician after a patient complains of back, neck or extremity pain. At right: The top disc has herniated, or "slipped," and is pressing on a nerve. A herniated disc can occur in the cervical spine (neck) or lumbar spine (lower back).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
